Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
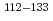 Sb
SbLechner, S.*; Miyagi, Takayuki*; Xu, Z. Y.*; Bissell, M. L.*; Blaum, K.*; Cheal, B.*; Devlin, C. S.*; Garcia Ruiz, R. F.*; Ginges, J. S. M.*; Heylen, H.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 847, p.138278_1 - 138278_9, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Ozu, Akira; Tachi, Yoshiaki; Arita, Yuji*
Reza Kenkyu, 42(12), p.913 - 917, 2014/12
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) analysis has been applied to the molten alloy production process, in which simulated metals (Zr, Cu, Sm, Ce) are used instead of nuclear metallic fuels contained minor actinide (MA), with the aim of in-situ monitoring the elementary composition of the surface of the molten alloy in a chamber and vapor particles generated from the surface of the molten alloy. The variation in the ratio of elementary composition of the surface of the molten alloy in the crucible was successfully observed depending on temperature of the crucible. The elementary composition of the vapor particles appeared in the molten alloy chamber was also measured. The practical experimental results show that LIBS technique is very useful for investigating the elementary composition in the process and understanding the behavior of molten alloy in the crucible.
Nagashima, Akira
Nihon Butsuri Gakkai-Shi, 56(3), P. 207, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
 and KY
and KY F
F
Wells, J. P.*; Sugiyama, Akira; Han, T. P. J.*; Gallagher, H. G.*
Journal of Luminescence, 87-89, p.1029 - 1031, 2000/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:47.77(Optics)no abstracts in English
Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAERI-Research 99-044, 16 Pages, 1999/07
no abstracts in English
 using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS)
using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS)Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Ito, Chikara; Takano, Masahide; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Thornton, B.*; Sakka, Tetsuo*; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
In the post-accident nuclear core reactor of the TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants, melted fuel core, fuel cladding and construction material (corium debris) might drop in the lower part of the reactor, which filled with seawater that was injected for urgent cooling. The major components of the debris material are assumed to be uranium oxide (UO , fuel core), zirconium alloy (Zry, fuel cladding) and iron (Fe, construction material). In this presentation, we report underwater analysis of simulated corium debris, (U,Zr)O
, fuel core), zirconium alloy (Zry, fuel cladding) and iron (Fe, construction material). In this presentation, we report underwater analysis of simulated corium debris, (U,Zr)O , by the transportable fiber-coupled LIBS instrument. The experiments were carried out using a wavelength region of 730-1100 nm for pulsed-lasers and plasma emission measurements, which shows no attenuation in the optical transmittance of the fiber optic cable by intense radiation dose. Based on the observed emission spectrum in the region of 750-870 nm, we determined candidates of the emission lines of Zr, U and Fe that are applicable to analyses of the debris without mutual interference. The LIBS spectra of five different concentration ratio samples for Zr/U were measured to obtain calibration data. We succeeded to obtain linear calibration data for emission intensity ratio versus concentration ratio of Zr/U.
, by the transportable fiber-coupled LIBS instrument. The experiments were carried out using a wavelength region of 730-1100 nm for pulsed-lasers and plasma emission measurements, which shows no attenuation in the optical transmittance of the fiber optic cable by intense radiation dose. Based on the observed emission spectrum in the region of 750-870 nm, we determined candidates of the emission lines of Zr, U and Fe that are applicable to analyses of the debris without mutual interference. The LIBS spectra of five different concentration ratio samples for Zr/U were measured to obtain calibration data. We succeeded to obtain linear calibration data for emission intensity ratio versus concentration ratio of Zr/U.
Aoyagi, Noboru; Watanabe, Masayuki; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 ray irradiation environment
ray irradiation environmentOba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Iwanade, Akio*; Wakaida, Ikuo; Ito, Chikara
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Murakami, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Ito, Chikara; Takano, Masahide; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Thornton, B.*; Sakka, Tetsuo*; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
To inspect the post-accident nuclear core reactor of the TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants, a transportable fiber-coupled laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) instrument has been employed. In the post-accident nuclear core reactor, melted fuel core, fuel cladding and construction material might drop in the lower part of the reactor, which filled with seawater that was injected for urgent cooling. The major components of the debris material are assumed to be uranium oxide (UO , fuel core), zirconium alloy (Zry, fuel cladding), stainless steel (Fe, construction material) and boron carbide (B
, fuel core), zirconium alloy (Zry, fuel cladding), stainless steel (Fe, construction material) and boron carbide (B C, critical control material). In this presentation, we report underwater analysis of simulated corium debris, (U,Zr)O
C, critical control material). In this presentation, we report underwater analysis of simulated corium debris, (U,Zr)O , and B
, and B C by fiber-coupled LIBS instrument. The experiments were carried out using near-infrared wavelength region for pulsed-lasers and plasma emission measurements, which shows no attenuation in the optical transmittance of the fiber optic cable by intense radiation dose. We determined candidates of the emission lines of Zr, U, Fe and B (BO) that are applicable to analyses of the debris without mutual interference.
C by fiber-coupled LIBS instrument. The experiments were carried out using near-infrared wavelength region for pulsed-lasers and plasma emission measurements, which shows no attenuation in the optical transmittance of the fiber optic cable by intense radiation dose. We determined candidates of the emission lines of Zr, U, Fe and B (BO) that are applicable to analyses of the debris without mutual interference.
Murakami, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iimura, Hideki
no journal, ,
Because nuclear charge radii have recently been calculated by including the 3-body interaction, it is interested very much to confirm experimentally this theory. Up to now, high-resolution laser spectroscopy is the only way to measure the charge radii of unstable nuclides. In this seminar, methods of the laser spectroscopy for unstable nuclides is given together with the procedure to determine the change of charge radii from the isotope shifts. Also, progress of laser spectroscopy experiments in radioactive beam facilities in the world is reviewed. Finally, I will discuss a plan of laser spectroscopy experiment in RIBF to confirm the effect of 3-body interaction on nuclear charge radii.
Kusaka, Ryoji; Watanabe, Masayuki
no journal, ,
Solvent extraction (liquid-liquid extraction) is a significantly important technique for the separation and purification of lanthanides. Because of the amphiphilic nature of extractants, such as di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid (HDEHP) used for the solvent extraction of lanthanides, the interface plays a crucial role as the site of the formation of lanthanide-extractant complexes and the subsequent transfer reaction to an organic phase. Here we studied the structure of a europium(III) (Eu ) complex with HDEHP formed at an HDEHP monolayer/water interface by heterodyne-detected vibrational sum frequency generation (HD-VSFG) spectroscopy. The vibrational spectra of the interface observed by HD-VSFG in the CH and OH stretching region demonstrate that not only HDEHP but also water molecules are bonded to Eu
) complex with HDEHP formed at an HDEHP monolayer/water interface by heterodyne-detected vibrational sum frequency generation (HD-VSFG) spectroscopy. The vibrational spectra of the interface observed by HD-VSFG in the CH and OH stretching region demonstrate that not only HDEHP but also water molecules are bonded to Eu at the interface. This structure of the interfacial Eu
at the interface. This structure of the interfacial Eu complex is intermediated between those of the complexes in the aqueous and organic bulk phases, suggesting that in the process of the solvent extraction of Eu
complex is intermediated between those of the complexes in the aqueous and organic bulk phases, suggesting that in the process of the solvent extraction of Eu by HDEHP extractant, Eu
by HDEHP extractant, Eu forms the intermediate complex with HDEHP and water at the interface and, subsequently, the transfer of Eu
forms the intermediate complex with HDEHP and water at the interface and, subsequently, the transfer of Eu into an organic phase occurs.
into an organic phase occurs.
Oba, Hironori; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Ouchi, Atsushi*; Mizusako, Fumiki*; Eto, Yoshinori*; Torimaru, Tadahiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iimura, Hideki
no journal, ,
So far the measurements of isotope shifts by laser spectroscopy is the only method to determine the nuclear charge radii. However, in order to deduce the nuclear charge radii, the atomic factor must be known. It is difficult to calculate the atomic factor precisely, and this causes some uncertainties for nuclear charge radii. Recently the world first facility for electron scattering for unstable nuclei, SCRIT, has become operational. It is expected that the elastic electron scattering data by SCRIT can improve precision of the nuclear charge radii in combination with the isotope shift data. In this presentation, present status of laser spectroscopy for unstable nuclei is reviewed, and the program which should be undertaken at SCRIT will be discussed.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
no journal, ,
Remote analysis of highly radioactive materials including actinide elements and fission products is a necessary technology for decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. However, due to the intense radioactivity, it is difficult for the analysis engineer to directly handle the analytical samples, and the application of traditional radiochemical analysis is considered to be difficult. Therefore, we are developing a remote analytical technique by combining atomic absorption spectrometry and laser ablation technique requiring no sample pretreatment. When a solid sample is irradiated with a intense laser pulse, part of the surface materials evaporates and is decomposed into monoatomic species to form an ablation plume. When another laser beam tuned to the resonance frequency of the isotope of interest is intersected with the plume, the isotope ratio can be determined from the comparison of the absorbance for each isotope since only the isotope atoms absorb the laser light. In order to reduce the effects of the Doppler effect and the Stark effect to realize sensitive and isotope-selective analysis, it is necessary to optimize the experimental conditions. Thus, we measured the absorption spectra with various experimental conditions, and investigate variations in the spectral line-width and the absorbance. The experimental conditions for higher sensitivity were determined from the laser-induced fluorescence image of the plume observed at various observation timing. By evaluating the analytical performance of U and Pu using the obtained optimum conditions, it was demonstrated that this analytical technique is applicable to the isotope analysis of decommissioning related substances.
Tajima, Minori*; Takamine, Aiko*; Iimura, Hideki; Wada, Michiharu*; Schuessler, H. A.*; Ueno, Hideki*
no journal, ,
Collinear laser spectroscopy is widely used to measure the isotope shifts and the hyperfine structures of unstable nuclei, from which the change of charge radii and the electromagnetic moments of these nuclei are deduced. However, radioisotopes of refractory elements have not been measured, because it is difficult to generate the ion beams necessary for collinear laser spectroscopy. Recently, SLOWRI has been constructed at RIKEN RI beam facility (RIBF), which can afford the ion beams of radioisotopes of all elements. We are developing a collinear laser spectroscopy setup at SLOWRI. We have confirmed that the reference values of the isotope shifts and the hyperfine structure constants of stable Ba isotopes were obtained. Since the intensities of radioisotopes are much lower than those of stable isotopes, improvement of sensitivity by using such as ion-photon coincidence is now in progress.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Iwata, Yoshihiro; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
no journal, ,
Laser ablation has been studied for application in many fields such as material processing and material creation. In the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, laser induced breakdown spectrometry (LIBS) based on ablation emission is expected to be used for the remote analysis of highly radioactive fuel debris and other materials. However, it is feared that LIBS alone will not provide sufficient nuclide resolution if the information on isotopic composition is required. In this study, we attempted high-resolution spectroscopy using an ablation atomic source by irradiating two resonance laser beams in opposition to a laser plasma cooled in a reduced-pressure gas and spectroscopy the resonant fluorescence from the highly excited state produced by two-step resonant excitation of atoms. As a result, it was found that the Doppler-free spectroscopy can narrow the linewidth of Ca to less than a few tenths of the conventional ablation resonance spectroscopy linewidth of about 2 GHz. This result shows the possibility of remote isotopic analysis even for nuclides with small isotope shifts, which have been difficult to measure in the conventional spectroscopy.